Events#
As discussed in Figgy Basics, many of Figgy's features are driven by Events.
The following event types are tracked:#
-
CloudTrail SSM Events: Source
- PutParameter
- DeleteParameter
- DeleteParameters
-
DynamoDb Stream Events: Source
- Any change to
figgy-config-replicationDyanmoDB Table.
- Any change to
These event streams trigger a number of features in Figgy including:
-
Maintaining records in the
figgy-config-cachetable. The Figgy CLI regularly queries this table inform its local cache. These names support the auto-complete functionality and browse tree in the Figgy CLI. -
Triggering
source→destinationreplication. If a source record is updated, Figgy will automatically trigger replication to all destinations. Likewise, if a newsource→destinationrecord is added, a DDB stream event will trigger immediate replication. -
Maintaining the Figgy audit log. The
figgy-config-auditortable maintains a history of all parameter changes over time. Every change to a parameter in ParameterStore results in a new record inserted into this table. Figgy is able to support point-in-time restores by leveraging the history of events stored in this table.
Why events?#
To improve the collaboratve user experience
Figgy is designed to support the collaboration of users across disparate teams. Live events enable the Figgy CLI to update
configuration state virtually instantly. For instance, if Aravind adds a new parameter to ParameterStore, events will
trigger that update our remote cache which informs Figgy's local state. If Shauna runs figgy config get ~1 second later she
will see Aravind's new parameter.
To keep desired state in-sync with actual state
Many features of Figgy are designed around users defining the desired state of their configurations. Leveraging native AWS events to drive these changes ensures remote state remains in sync with desired state as quickly as possible.
Event Sourcing
Event Sourcing is a design pattern where a log of events is the source-of-truth for application state. If application state needs to be restored or repaired, a series of events can be replayed to reset the state instead of attempting restoring data from a historical snapshot. Adopting this pattern enables Figgy to replay events to rebuild both current state and historical state in disaster recovery scenarios. Essentially, because all events are captured, we can track all changes over time, and restore any, or all, ParameterStore values to any point-in-time in the past.
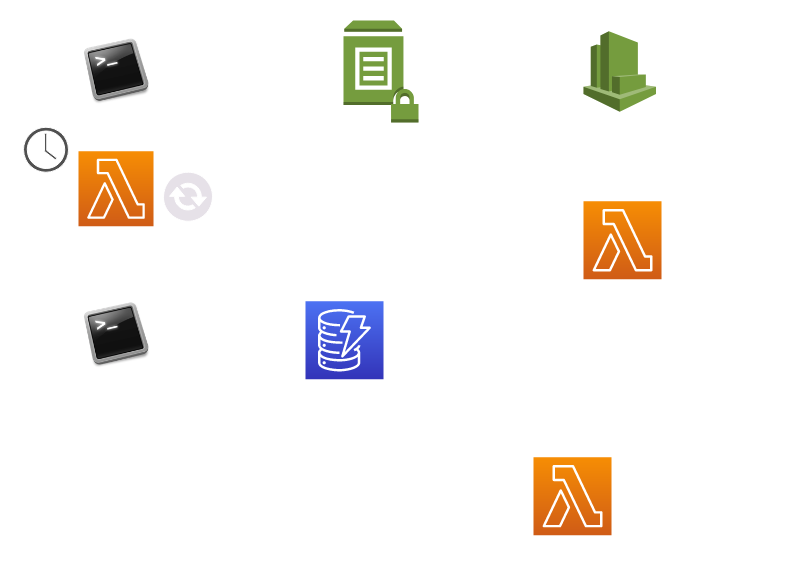
Event Flow#
The put and sync commands enable users to add or overwrite values in ParameterStore. These values trigger events that are
pushed to the CloudWatch event bus via CloudTrail. All ParameterStore changes are consumed by the three Lambda functions
depicted below.
-
Config Cache Manager - Listens to PS Change events and maintains a cache of PS Names (not values) that is used to inform functionality in the Figgy CLI.
-
Parameter Stream Replicator - Listens to PS Change events. If the changed value is a
sourceof replication, this function will re-trigger replication to all downstreamdestinations. -
Parameter Store Auditor - Listens to PS Change events and logs changes to our
figgy-config-auditorDynamoDB table.
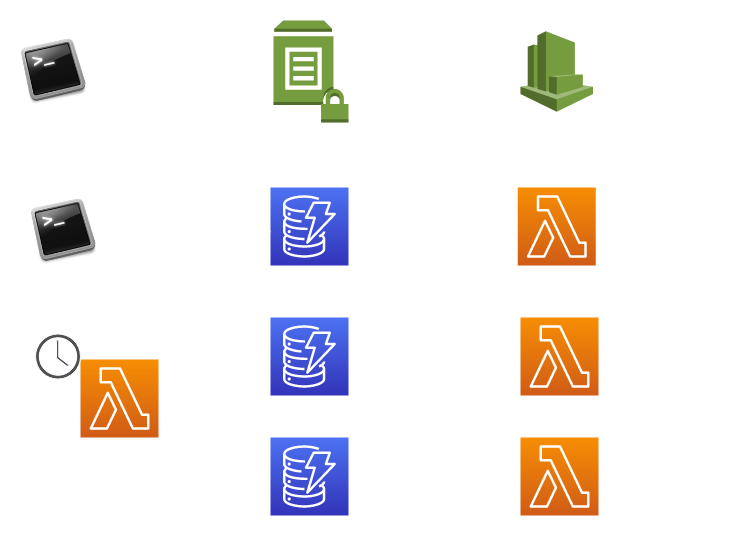
Replication Event Flow#
Replication can be triggered one of three ways:
- A
sourceof replication is updated, thereby triggering downstream updates. - A new record defining
source→destinationreplication is inserted into theservice-config-replicationDynamoDB Table. - The Replication Syncer lambda detects an out-of-sync replication source and destination and synchronizes these values.
The Replication Syncer Lambda will do nothing in the vast majority of cases. It is mainly there as a stop-gap in case a bug is introduced or a user accidentally breaks the the former 2 lambdas.